Emissions markets, also known as carbon markets, are financial mechanisms designed to reduce carbon emissions by setting a cap on pollution, assigning allowances to energy consumers, and trading those emissions allowances. These markets play a critical role in energy policies aimed at combating climate change by providing economic incentives for reducing carbon emissions. This article explores the concept of emissions markets, how they function, their key components, benefits, challenges, and overall impact on the environment and economy.
What Is An Emissions Market?
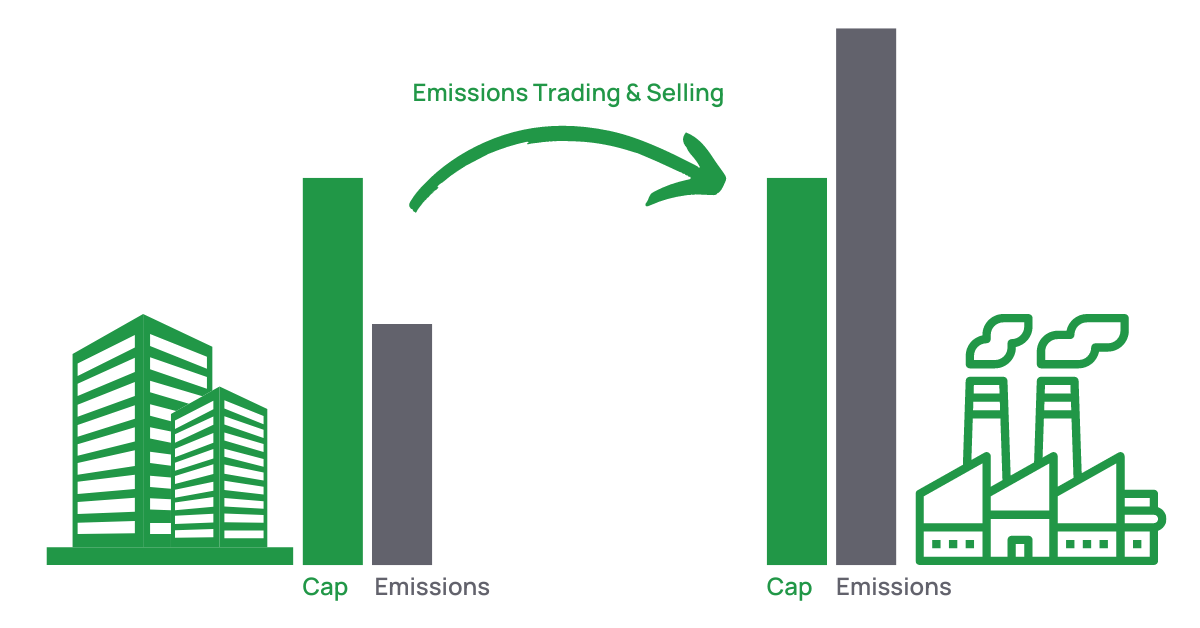
An emissions market, often referred to as a carbon market, is a system where carbon emissions trading occurs. It operates on the principle of cap and trade, where a limit (cap) is set on the total amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted. Tradable allowances are then issued for all emissions under the cap. These allowances can be bought and sold to other organizations that are unable to be under their cap, creating a financial incentive for reducing emissions.
The 10 Key Components Of An Emissions Market
Emissions markets are structured to efficiently reduce pollution by setting caps and allowing for the trading of emissions allowances. Here are the ten key components that make up an emissions market:
1. Cap On Pollution
The fundamental aspect of an emissions market is the cap, which is a regulatory limit on the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions that can be emitted by all participating entities. This cap is typically set by a government or regulatory body and is designed to decrease over time to continue to reduce overall emissions.
2. Tradable Allowances
Within the cap, emission allowances are distributed to the participating entities. Each allowance permits the holder to emit a specific amount of greenhouse gases, usually measured in tons. These allowances can be allocated for free based on historical emissions (grandfathering), auctioned to the highest bidder, or a combination of both.
3. Allowance Trading
A critical feature of emissions markets is the ability to trade allowances. Entities that reduce their emissions below their allowance can sell their surplus to other entities that need to cover excess emissions. This creates a financial incentive for companies to reduce their emissions cost-effectively and fosters a dynamic trading market based on supply and demand.
4. Compliance And Monitoring
Participants must monitor and report their emissions accurately and regularly. Independent verification ensures that reported emissions data is accurate. At the end of each compliance period, entities must hold enough allowances to cover their actual emissions or face steep penalties.
5. Banking And Borrowing
To provide flexibility, some systems allow the banking of surplus allowances for future use or borrowing allowances from future periods. This feature helps entities manage their compliance strategies more effectively and incentivizes early reduction in emissions.
6. Offset Credits
In addition to allowances, entities can generate or purchase offset credits by investing in projects that reduce emissions. These projects can include renewable energy installations such as solar, reforestation, or carbon capture and energy storage. Offset credits can be used to meet a portion of compliance obligations, providing an additional mechanism for emissions reduction.
7. Market Oversight
Effective oversight by regulatory bodies ensures the integrity of the emissions market. This includes monitoring trading activities to prevent fraud, ensuring transparency, and maintaining market stability.
8. Technology Standards And Benchmarks
Regulations also include technology benchmarks that require the use of the best available technology not entailing excessive cost (BATNEEC). This ensures that emissions reductions are achieved using the most effective, economically viable, and accurate technologies available.
9. Incentives For Energy Efficiency
The emissions market inherently encourages companies to improve energy efficiency as a cost-effective way to reduce emissions. This has led to innovation and the development of new energy technologies and practices that further reduce greenhouse gas outputs.
10. Renewable Future
As a result of the carbon emissions market, the world is moving towards a more sustainable and renewable energy future. Reducing carbon emissions is now a common practice among the largest energy users and this practice of mandating emissions reductions is fostering a climate of energy efficiency.
How Do Emissions Trading Mechanics Work?
Emissions trading mechanics involve a series of steps and mechanisms designed to control and reduce pollution. Here’s a detailed look at how this system operates:
1. Establishing the Limit
A governing or regulatory body sets a cap on the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions allowed within a specific period by an organization. This cap is typically based on scientific and economic assessments aimed at reducing overall emissions over time. These caps can be based on building square footage, energy usage type, or industry-specific.
2. Distribution Of Allowances
The total emissions cap is divided into allowances, each representing the right to emit a specific amount (e.g., one ton) of greenhouse gases. These allowances are often allocated to specific companies based on historical emissions. In some markets, auctions are held where companies can bid on total allowances and these credits are auctioned to the highest bidder. In all circumstances, each individual organization has a carbon allowance that defines how much greenhouse gas they can emit. If they do not use this allowance, they can sell it to someone else who has the demand.
3. Carbon Trading Mechanics
In most countries where carbon credit trading occurs, a market is established where these allowances can be bought and sold. Companies that expect to exceed their emission limits can buy additional allowances from those who have reduced their emissions below their allocated amount.
These markets operate on various platforms, including government-run exchanges, private markets, or international trading platforms. The price of allowances fluctuates based on supply and demand, creating an economic incentive to reduce emissions and contribute to the renewable energy transition.
The Benefits Of An Emissions Market
There are many benefits that have come about as a result of emissions trading and carbon reduction. Some of those benefits include:
Environmental Certainty
By setting a firm cap on emissions, the system ensures that environmental goals are met, reducing overall pollution levels.
Economic Efficiency
Emissions trading provides flexibility for companies to choose the most cost-effective way to reduce emissions, promoting energy efficiency and innovation.
Incentives For Reduction
Companies have financial incentives to reduce emissions early and bank surplus allowances for future use, fostering ongoing environmental improvements.
Revenue Generation
Governments can generate revenue through the auctioning of allowances, which can be reinvested in further environmental and energy projects. Companies can generate additional revenue by selling excess allowances to other organizations that are in need.
The Challenges Of An Emissions Market
On the other hand, there are many challenges faced by companies and regulators to implement and maintain these markets. Let’s explore some of the cons of the emissions markets in more detail:
Market Volatility
The prices of tradable allowances can be volatile, leading to uncertainty for businesses planning long-term investments.
Implementation Complexity
Setting up and maintaining emissions trading systems requires significant regulatory oversight and administrative costs.
Potential For Market Manipulation
There is a risk of companies gaming the system, buying cheap allowances to avoid making real emissions reductions. There is also a concern over fraud as companies need to reduce emissions or be penalized.
Equity Concerns
The costs associated with emissions trading can disproportionately affect certain industries and communities, raising concerns about fairness and social equity.
Want To Learn More About Energy Policy Around Carbon Emissions?
Emissions markets, through carbon emissions trading and other mechanisms, offer a flexible and economically efficient approach to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. While they come with challenges such as market volatility and implementation complexity, the benefits make them a valuable tool in global efforts to combat climate change. As energy policies continue to evolve, emissions trading schemes will play a crucial role in promoting sustainability and energy efficiency. Our team of energy experts has helped many of our commercial and industrial customers navigate the world of emissions trading and carbon offset. Contact us today for more information.