Commercial electricity rates are a complex mix of generation costs, transmission congestion constraints, capacity prices, and local market dynamics. In deregulated energy states, these rates can vary drastically between regions and even from building to building. In this article, we aim to outline the fundamental elements of a commercial electricity rate, how each price component is calculated, and strategies to reduce or manage your business electricity rates.
Key Factors That Influence Commercial Electricity Rates
There are several key factors that influence commercial electricity rates. Let’s explore some of these core cost factors in more detail below.
Generation
The physical generation of electricity affects the underlying cost of the electric commodity. This cost component determines approximately 50% of the total retail supply price for electricity and is greatly impacted by market forces. Fuel costs, such as the price of natural gas, influence the price to produce electricity using a natural gas peaker plant. Furthermore, outline factors such as weather, economic growth, and geopolitical events can greatly impact supply and demand dynamics in this market and swing the price of electricity.
Transmission
Transmission costs are determined by the price to move electricity across high-voltage lines from one location to another. While transmission rates are regulated and set based on dollars per megawatt per year ($/MW/year), congestion on regional transmission pathways can drive up local electricity prices in certain areas of the electric grid. For example, the annual cost to transmit one megawatt (MW) of electricity in the PPL region in Pennsylvania is approximately $104,055; however, there could be additional costs associated with transmitting power into specific zones within the larger PPL territory. These costs, known as congestion, tend to drive price differentials between zones. In an effort to hedge this price risk, retail energy suppliers often utilize financial transmission rights (FTRs) contracts.
Capacity
Capacity costs are determined annually in most markets through a base residual auction where generators bid on the price to meet future expected demand. These fees are paid to generators to be on “standby” at all times, and the fees are remitted whether the generators are actively generating power or not. Capacity is often thought of as an insurance policy to guarantee the grid has enough electricity to meet demand at all times. In most ISO/RTO markets, capacity costs for individual businesses are calculated based on the business’s peak demand each summer. The business, in turn, will pay the local capacity rate multiplied by its peak demand. Since capacity costs are often bundled into fixed rates by suppliers, a facility’s load factor (a ratio of its peak demand to annual usage) plays a critical role in determining the total price for electricity.
Recently, the PJM region saw a drastic increase in capacity rates due to increased demand and decreasing available generating capacity. In an effort to combat prices, FERC implemented a capacity price cap in 2025. The PJM capacity price cap was then reached for the 2026/27 base residual auction, indicating that prices will remain high for several years into the future.
Ancillary Services
Ancillary services are additional costs placed on ratepayers in most RTO/ISO markets. These wholesale markets were constructed in a further attempt to deliver grid stability. In ancillary services markets, generators can participate and get paid for supporting the grid when power is needed urgently. This includes voltage support, generating reserves, and more. Ultimately, the price of ancillary services is passed to the end user and can make up a small percentage of the total price for electricity.
How Time-Of-Use Impacts Commercial Electricity Costs
In most wholesale electricity markets, commodity prices are divided into on-peak and off-peak periods. In the PJM market, for example, on-peak hours are from 7:00 AM to 11:00 PM (Monday-Friday), while off-peak hours are 11:00 PM – 7:00 AM (Monday-Friday) and both Saturday and Sunday. Off-peak prices typically trade at lower costs since there is usually less demand for electricity during these times.
Businesses with significant off-peak energy usage might benefit from choosing a time-of-use utility tariff or by entering into a time-of-use retail electricity supply agreement. Many large energy consumers, for example, elect for hybrid energy products, such as block + index plans, that allow them to float their off-peak power usage on the low-cost index market. Rather than paying a premium for an around-the-clock fixed price, these businesses can take advantage of market and usage dynamics to save on energy costs.
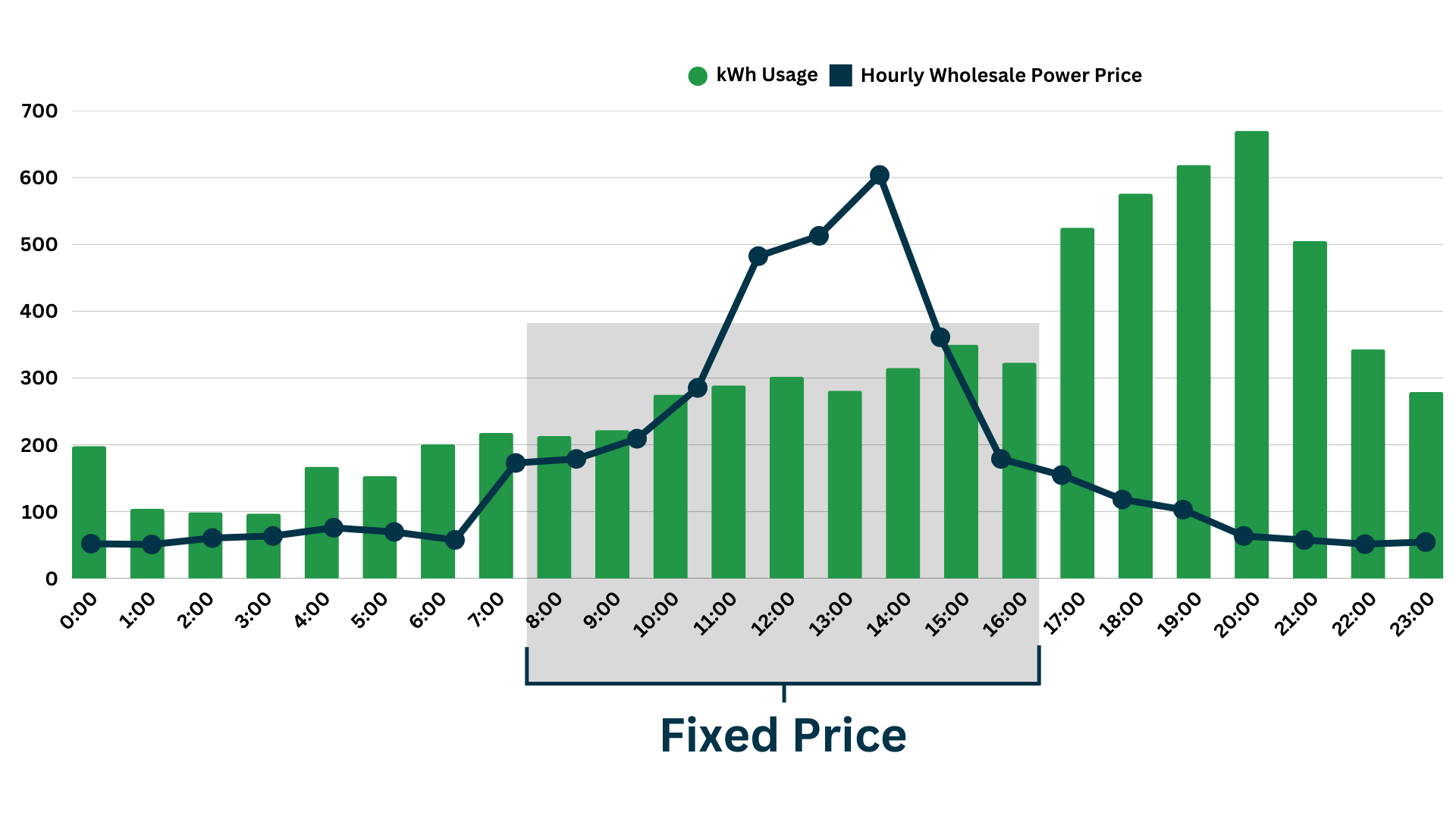
In this chart above, a majority of the business’s electricity consumption is at night when wholesale index prices are low. The business made a good decision by entering into a block + index retail electricity supply contract that allowed them to fixed their costs during volatile, on-peak hours, and float on the index market for the rest of the day. Compared to a standard fixed price, this facility should be saving considerable amounts of money each year.
How Diversegy Helps Businesses Optimize Their Power Rates
Commercial electricity rates are influenced by many moving parts, which can make managing costs challenging for businesses. Diversegy helps simplify this complexity by providing detailed bill analysis and cost breakdowns, giving companies clarity on what drives their rates. Our team sources the best suppliers and negotiates contracts that balance cost savings with long-term stability. Beyond cost control, we integrate risk analysis into procurement strategies so that businesses can meet financial objectives without taking on too much exposure. By taking a proactive approach to electric rate optimization, companies can avoid unnecessary expenses and gain more control over their energy strategy. If you want expert guidance tailored to your business, contact our team of electricity market experts today to explore smarter procurement solutions.