It’s the job of electric grid operators to keep a continual balance of electricity supply and demand in order to avoid blackouts and keep the grid running reliably. But, balancing consumer energy demand can be challenging. Energy demand is volatile and changes with the weather, seasonality, economic conditions, and geopolitical trends. So how do grid operators ensure that there is a reliable stream of electricity to always meet demand? The answer is electric capacity. This article aims to outline electric capacity, capacity markets, and how capacity is used to ensure a reliable supply of power.
What Is Electric Capacity?
Electric capacity, by definition, is the total amount of electricity generation available for consumption at any given time. To ensure that there is a sufficient amount of capacity available to supply consumers, electric grid operators created capacity markets to incentivize electric generators to make enough power. Here’s how they work…
Capacity Markets
Power capacity markets exist in almost every regional electricity transmission network, with the exception of ERCOT in Texas although Texas state regulators are in talks of forming a capacity market. These markets operate by charging energy consumers a fee, often part of their total electricity supply cost, and passing those fees on to electricity generators. You see, power generators have no incentive to make power when prices are low. So, in order to ensure that there are enough power plants making electricity at all times, capacity markets pay generators for their “electric capacity”.
ERCOT Electric Capacity Issues
There is a heated debate over the role of capacity markets in Texas after Winter Storm Uri in 2021. Texas is one of the only states to not institute an electricity capacity market, so electric generators have no incentive to always remain reliable. During the storm, many electric generators went off line and there was not enough electricity to power homes and businesses. This caused rolling blackouts across Texas and some people were left without power for days.
Texas and ERCOT regulators are voting on potentially implementing a capacity market in order to avoid disastrous issues like this in the future. With a capacity market in Texas, power generators would earn revenue in exchange for their commitment to be available to generate electricity at all times.
Types of Power Capacity
Capacity, as it relates to electricity, can be any available source of electricity generation. This can include:
- nuclear power plants
- coal
- natural gas electricity generation
- wind
- hydroelectric
- solar
- and other forms of renewable generation.
In addition to these methods of generating electricity, capacity also exists when end users consume less electricity. Remember that electricity supply and demand need to be in constant balance, so when less power is being consumed, then less needs to be made. Grid operators view a reduction in power consumption as equivalent to power being generated. In fact, demand response programs will pay consumers for reducing electricity consumption during times of peak demand on the electrical grid.
How Is Capacity Measured And Billed?
Electrical capacity market rates are set through capacity auctions. These auctions are held by grid operators and set capacity rates up to three years into the future. During capacity auctions, electricity generators and demand response companies place bids for the total amount of electricity capacity they will deliver at certain times of the year. This ensures the grid operator that there will be enough electricity to meet consumer demand. If they are not able to meet their bid commitments, they are then assessed large financial penalties.
Consumers are charged for capacity as a part of the electricity supply cost. Typically, these costs are collected by retail electricity suppliers and/or electric utility companies and then remitted to the electric grid. Capacity rates are billed based on a consumer’s total peak demand, in kilowatts or kW. In some markets, like PJM, capacity rates are based on an average of a consumer’s kW demand on the five peak days each summer. Other markets, like NYISO, capacity rates are calculated using a consumer’s peak hour from the previous year. These kW ratings are then multiplied by the capacity auction rate and total costs are spread out over the consumer’s total electricity bills for the year. This is how peak capacity rates have a direct effect on load factor ratings.
Why Is Capacity Important To Consumers?
If you’re operating a business that relies on electricity, you might not realize how critical capacity is to your daily life. Capacity markets in deregulated energy states allow for the continual reliable supply of power for your business operation. Without capacity, grid blackouts and other power supply interruptions would be inevitable.
Capacity costs can also account for up to 40% of a consumer’s total electricity supply costs. And when dissecting the anatomy of an electricity bill, you can see that electricity supply costs can account for up to 70% of the total bill. So, controlling capacity costs is critical to lowering energy expenses. Here are some tips for shaving peak demand, lowering capacity expenses, and ultimately reducing energy costs at your business:
- Conduct an energy audit
- Enroll in a demand response program
- Stagger motor schedules
- Retrofit your building with LED lighting
- Resequence building automation systems
- Install commercial solar
These suggestions are a good starting point for lowering energy consumption and peak demand for your commercial facility. It’s best to contact an energy efficiency professional or energy brokerage firm that specializes in helping its customers reduce energy expenditures.
How Electric Capacity Auctions Work
Capacity markets function through an auction where each electric generation source, from old nuclear plants to new wind turbines, bids based on its total operational costs. And, bidding in capacity auctions varies significantly. Older plants might bid low due to depreciated costs, whereas new installations bid higher, factoring in both capital and operational expenses.
The grid operator predicts electricity demand for a three-year period in the future, aiming to secure sufficient capacity at the lowest cost. In this auction, all resources bid their total cost of operation, and the bids are arranged from lowest to highest until enough capacity is secured to meet projected demand plus a capacity risk margin.
For example, if a hydro-electric plant bids 50 megawatts at $30 per megawatt, and the highest necessary bid to meet demand is $150 per megawatt from a coal plant, all resources receive the $150 per megawatt, known as the clearing price. This mechanism ensures all committed resources are available when needed, even if a higher-priced resource sets the market rate. Here is an example of how a capacity auction might work:
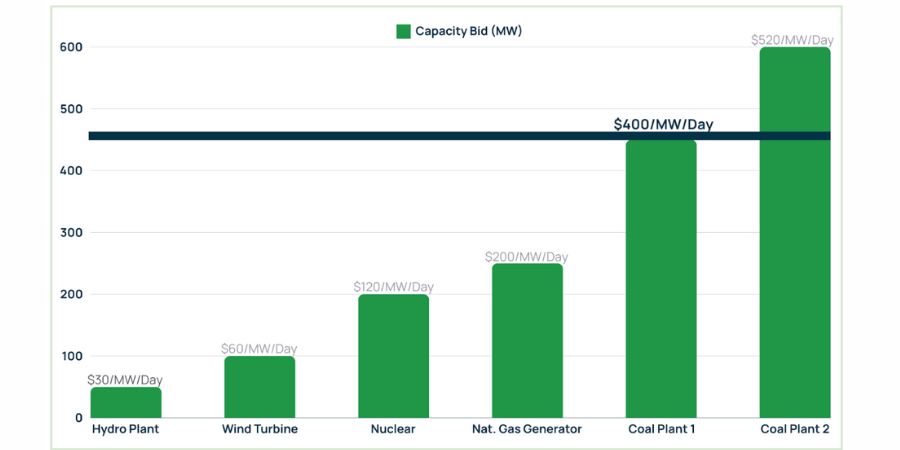
This setup encourages lower-cost, efficient resources to enter the market, potentially lowering overall prices and fostering investment in diverse energy assets. This system’s dynamics are pivotal for shaping the future electricity supply, and balancing cost efficiency and energy diversity.
Incremental Capacity Auctions
The core concept in capacity markets, such as those in the PJM territory, is that power plants are compensated for the capacity they promise to deliver in the future. These markets operate through an annual Base Residual Auction, which sets commitments for delivery three years later. Leading up to the delivery date, smaller Incremental Auctions allow participants to adjust their commitments by buying or selling capacity. This flexibility is crucial if a provider cannot meet its original commitment and needs to secure replacement capacity.
It’s important to note that in these auctions, there is no distinction between a megawatt generated by a power plant and a megawatt saved through efficiency or demand response. Thus, while I’ve referred to “power plants” for simplicity, demand-side resources are equally eligible to participate in these auctions.
In retail electricity supply agreements, it is critical to note capacity adjustment clauses that allow retail suppliers to pass through additional capacity incremental auction costs. This should not affect customers on short-term electricity contracts, but for multi-year contracts, capacity adjustment pass throughs are quite common.
Current PJM Capacity Costs
PJM Interconnection’s recent capacity auction saw prices drop by 15% across most areas. Despite this overall decrease, there were price increases in five regions due to transmission constraints and reduced supply offers kept the auction’s total cost unchanged at $2.2 billion. Here is a map of the current PJM capacity regions and their current costs in dollars per megawatt-hour ($/MWh):
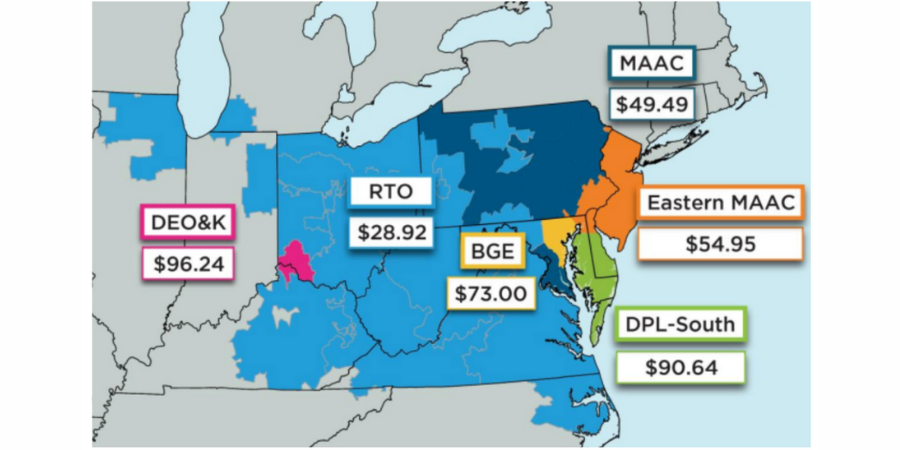
In a significant rule change approved by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, PJM adjusted market rules mid-auction to prevent a drastic price spike in the DPL-South Zone.
Challenges such as supply chain issues and land acquisition have slowed new generation development, despite over 40,000 MW of projects having cleared interconnection processes in PJM.
Need Help Measuring or Managing Capacity Costs?
Our team of energy market professionals monitors energy capacity auctions and market prices so we can better advise our customers. If you are looking for ways to reduce costs, capacity expenses are a great place to start. Contact us today so we can audit your capacity ratings and total costs.





