The use of fossil fuels in power generation has been a cornerstone of the energy grid and supply system for over a century, powering economies and shaping the industrial landscape of counties. Despite growing environmental concerns, push towards renewable energy, and the great energy transition, coal, natural gas, and oil continue to dominate the energy mix, providing the bulk of electricity generation worldwide. In this article will explore the enduring reliance on fossil fuels for power generation, examining the role of fossil fuels in the electric markets, the controversy surrounding fossil fuel-generated power, and the future outlook of the global energy transition.
Fossil Fuels And Their Role In Power Generation
Fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, and oil, have been and are currently a major source of electricity generation throughout the world. Power generation plants burn these fossil fuels to generate electricity. This is done through a process that converts the fossil fuel chemical energy into electrical energy from heat. The power generation process using these fuels typically follows this process:
- Combustion: Fossil fuels are burned releasing a significant amount of heat.
- Heat Transfer: The heat generated is used to boil water in a boiler, producing high-pressure steam. It might also directly drive gas turbines.
- Steam Turbine (coal and oil): The high-pressure steam is directed to a steam turbine, where it expands and cools. As the steam passes through the turbine blades, it causes the turbine to spin, generating power.
- Gas Turbine (natural gas): In natural gas power plants the burning gas directly spins a turbine. This process is more efficient than steam turbine systems.
- Power Generation: The turbine is connected to a generator. As the turbine spins, it turns the generator, which converts the mechanical energy of the spinning turbine into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
In 2022, fossil fuels accounted for 61% of all power generation worldwide. And, this number seems to be growing as evidenced by the chart below:
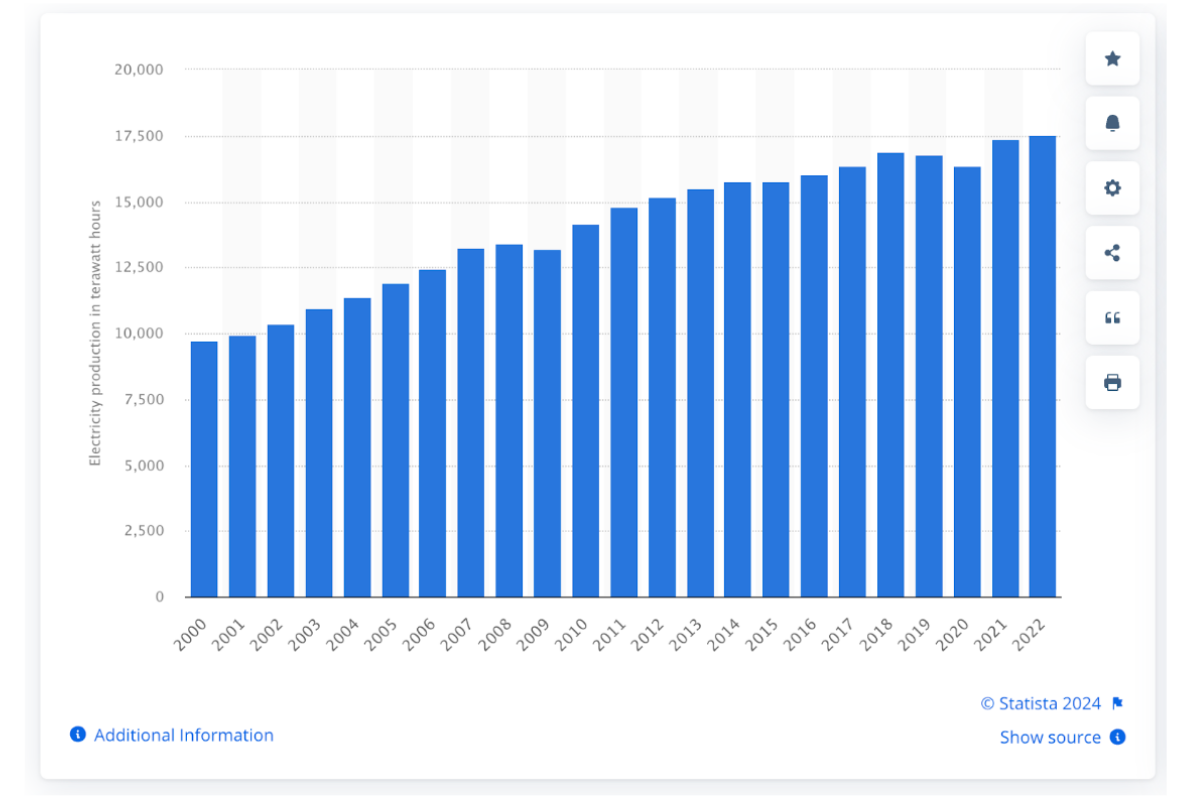
In 2023, it is estimated that fossil fuels still accounted for over 60% of all global power generation. This number is alarming for climate activists who are pushing for the clean energy transition and a move away from fossil fuel power sources.
Controversies Surrounding Fossil Fuel Power Generation
There are several controversies surrounding fossil fuels and their role in power generation. These controversies spands an array of topics from environmental concerns to energy grid security. Let’s look at some of the major challenges facing fossil fuel power today.
Environmental Impact & Climate Change
The most significant controversy stems from the environmental damage caused by extracting and burning fossil fuels. This includes air and water pollution, geological destruction from fracking and drilling, and the release of carbon gases that contribute to climate change.
Furthermore, the link between fossil fuel combustion and global warming is a major source of debate. The burning of coal, natural gas, and oil for power generation is a large source of global CO2 emissions. Coal-fired power plants, for example, are among the largest sources of carbon dioxide emissions.
Health Concerns
Fossil fuel power generation is also associated with health risks due to air pollution. Emissions from power plants include particulate matter that can lead to respiratory diseases, heart conditions, and other health problems. The health impacts often disproportionately affect communities located near the power plants.
Economic Issues
Because the fossil fuel industry is a significant source of employment, movements to reduce dependence on fossil fuels often face opposition. Many communities rely on drilling jobs, mining jobs, and jobs at the power plant. In certain parts of the country in the coal belt, this has become a major political talking point and driver for local votes.
Energy Security
Fossil fuels, although a very reliable source of power generation, are coming into light as the security of the grid is becoming a hot topic of debate. The centralized energy grid, supported by fossil fuel and nuclear generation, is vulnerable, outdated, and in need of serious investment. Proponents of distributed energy systems argue that localized wind, solar, and geothermal is a safer alternative for the future.
Energy Price Impacts
While the push for renewable energy is underway, the economic argument for fossil fuels keeps them burning. Fossil fuel power generation is still relatively inexpensive, although the cost of renewable energy has decreased drastically over the last decade. In addition, fossil fuel generation is still required to meet the baseload of electricity demand as renewable energy sources do not account for enough power capacity. Let’s look at the levelized cost of energy generation below:
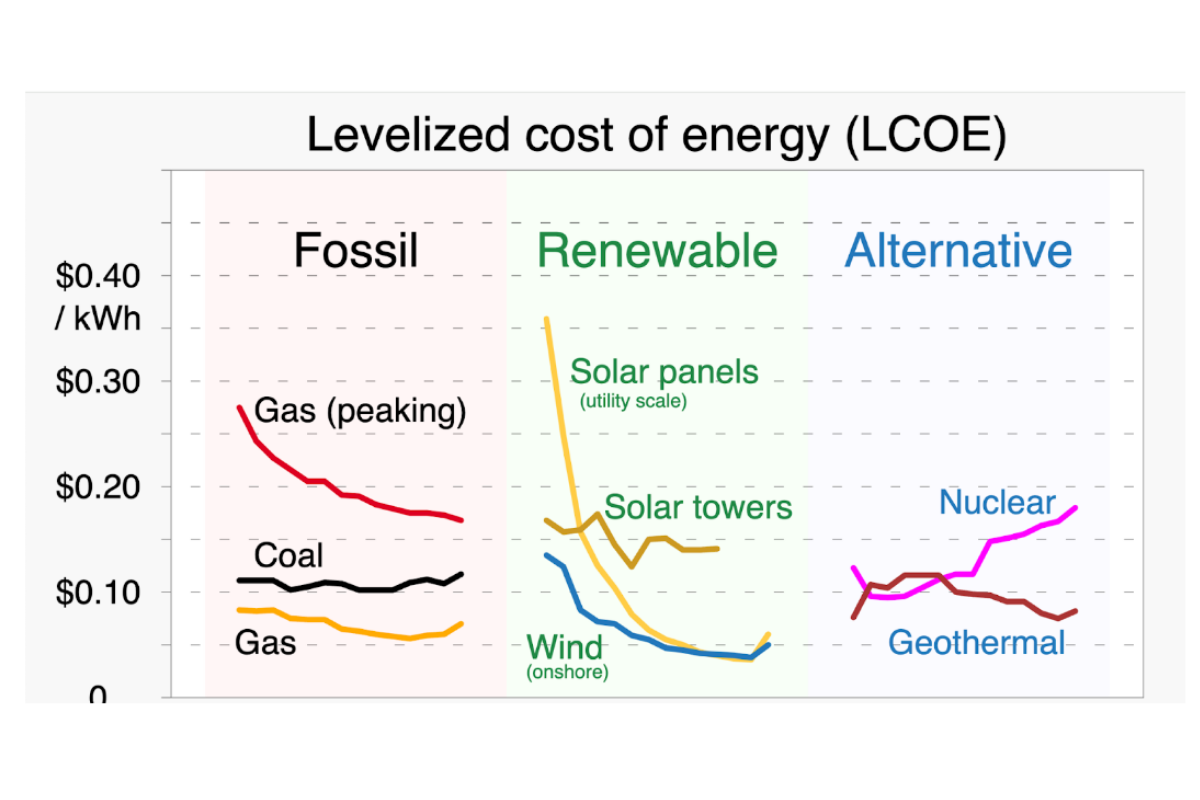
The Future Of Fossil Fuel Power Generation
As the world moves towards a more sustainable energy future and transitions to greener sources of energy generation, fossil fuels are at risk. Although many energy market experts argue that the reliance on fossil fuels is not going away soon, activists are pushing for legislation that will make this type of power generation harder and harder. Let’s look at some recent legislation and government movement as a precursor for the future of fossil-fuel-generated power.
Paris Agreement
Countries around the world have been working at implementing their strategies to meet commitments made under the framework of the Paris Agreement. This agreement was made to strengthen the global response to climate change.
Net-Zero Emissions Goals
Many countries have set net-zero carbon emissions goals for 2050 or earlier, with short-term targets for 2030. These goals typically require a drastic reduction in fossil fuel consumption, increased energy efficiency, and a major shift towards renewable energy.
Renewable Energy Incentives
Many governments have been enhancing or introducing new regulations and incentives to promote renewable energy development. This includes tax credits, cash subsidies, and bonus depreciation.
Carbon Emissions Trading
Carbon trading and price systems, including carbon taxes, have been adopted to incentivize emission reductions. The EU’s Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is one example. This allows companies to get credits for reducing carbon emissions that become saleable to other companies in need of credits.
Energy Efficiency Standards
There are many new laws aimed at promoting energy efficiency in buildings. These include standards for new construction, requirements for retrofitting of older buildings, and bans on natural gas in new buildings.
Fossil Fuel Subsidy Reforms
There has been increasing pressure to phase out subsidies for fossil fuels. Some countries are attempting to pass legislation that would redirect these subsidies towards renewable energy and energy efficiency projects.
Given the rapidly evolving nature of energy and climate policy, it’s likely that additional measures will be introduced or proposed in 2024, making it a rocky road ahead for the fossil fuel industry.
Would You Like To Pursue A Renewable Energy Strategy?
Not only can our team help you to arrange for the supply of renewable energy to your business or organization, we also offer an array of energy efficiency and renewable power solutions. Whether you are looking to reduce your peak load or want to explore a commercial solar project, we can guide you through your options and help you to create an effective energy strategy.