As the energy economy adopts renewable energy, wind and solar generation are becoming viable market participants. The variable renewable energy (VRE) aspects of these types of electricity generation, however, present many challenges for grid operators and utilities alike. The intermittent nature of renewable energy makes renewable integration into the power system very difficult. The fluctuations in energy production from VRE assets require system operators to adopt new energy policies to ensure their seamless incorporation. In this article, we will explore what a VRE is, the challenges it presents, and the solutions to make widespread adoption possible.
What Does VRE Stand For In Renewable Energy?
Variable Renewable Energy (VRE) refers to electricity generated from renewable sources like wind and solar power, where electricity output fluctuates due to weather conditions. Unlike conventional fossil fuel power plants, which generate electricity on demand, VRE generation depends on sunshine and wind. Some key characteristics of VRE assets include:
- Intermittent Supply: Energy production varies depending on wind speeds, sunshine, and weather conditions.
- Grid Integration: Requires generation forecasting and advanced energy analytics for power grid stability.
- Decarbonization: Plays a key role in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and achieving clean energy goals.
Sources of Variable Renewable Energy include:
Wind Power
Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from the wind into electricity. Wind farms are deployed both onshore and offshore, with offshore installations often providing more consistent power output. Fluctuating wind speeds can lead to inconsistent power generation and grid congestion when turbines overproduce.
Solar Power
Solar energy is captured through photovoltaic (PV) panels and converted to usable electricity through an inverter. These technologies generate electricity when sunlight is available, making solar highly dependent on weather conditions and seasonal changes. Solar power drops at night and requires coupled energy storage systems for seamless grid integration.
Other VRE Sources
While wind and solar power dominate VRE, other sources such as run-of-river hydropower and tidal energy also exhibit variability. These sources contribute to the renewable mix but face location-based constraints that limit widespread deployment.
What Is The Integration Of Variable Renewable Energy Sources?
Renewable integration refers to the process of incorporating variable renewable energy sources into the power system. Since the electric grid needs consistent voltage and current to avoid outages, integrating wind and solar requires balancing mechanisms that compensate for output fluctuation.
For example, if a solar system is producing too much electricity during a period of low demand, it can create an imbalance in the total electric system. The system output would need to be shut off, or clipped, during this period in order to avoid an oversupply. Many solar developers are designing battery-coupled systems that can capture this excess energy, not allowing it to be wasted. The battery can then discharge at a later time when energy is needed and earn additional revenue.
Challenges Of Integrating VRE
There are many challenges associated with renewable energy generation and its integration with the modern transmission system. Some of these challenges include:
Grid Stability & Reliability
A major challenge with variable renewable energy is maintaining power grid stability. Grid operators must ensure that supply meets demand at all times and have to plan for intermittent power generation. Some common solutions to this challenge include battery storage and smart grids using AI and real-time energy analytics to balance loads dynamically.
Forecasting & Planning
Advanced forecasting is critical for managing the day-ahead and real-time wholesale electricity markets in deregulated states. It can be hard to forecast intermittent renewable energy generation as a simple shift in the wind or change in weather can throw off the forecast. Today, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being used to predict solar and wind conditions with greater accuracy, helping grid operators plan for variations.
Transmission & Distribution Constraints
Many regions lack the transmission infrastructure to transport renewable energy efficiently. These lines are congested with existing electricity generation and need to be expanded to allow for new power sources. Building new transmission lines and investing in grid modernization are becoming essential for optimizing VRE integration.
Energy Market Adjustments
Electricity markets need pricing mechanisms that reflect the variability of renewables. Excess renewable energy production in a certain zone can greatly impact financial transmission rights (FTR) contract values and play a direct role in congestion pricing. These factors are influencing the traditional market operations of the electricity grid.
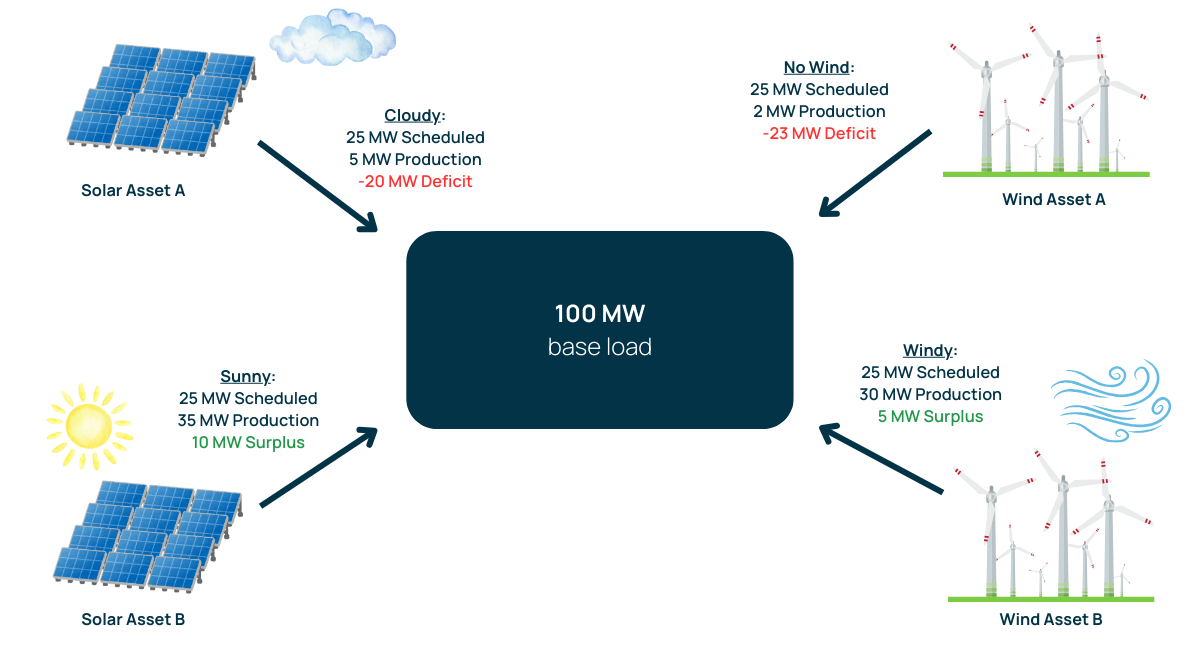
In the example above, there are 4 renewable energy generating assets scheduled to meet 100 MW of base electricity load. Due to sun and wind conditions, the total asset production is not enough to meet the scheduled load. In this scenario, the grid operator would need to turn on alternative production, such as a natural gas peaker plant in order to meet demand.
| Asset | Scheduled Power | Power Production | Deficit / Surplus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Asset A | 25 MW | 5 MW | -20 MW |
| Solar Asset B | 25 MW | 35 MW | +10 MW |
| Wind Asset A | 25 MW | 2 MW | -23 MW |
| Wind Asset B | 25 MW | 30 MW | +5 MW |
| Total | 100 MW | 72 MW | -28 MW |
Impact Of VRE On Energy Projects & Customers
The shift to variable renewable energy has spurred significant global energy investment in wind and solar projects. As governments and corporations set aggressive carbon reduction goals, demand for VRE is expected to rise. This is also having a big impact on energy customers including:
- Lower Costs: VRE can reduce long-term electricity expenses. Over time, renewable energy is the lowest-cost generation source from a cost of fuel perspective.
- Energy Independence: Businesses that install solar or wind can decrease reliance on utilities, developing on-site microgrids comprised of solar, wind, and battery assets.
- Sustainability Benefits: Many organizations can now invest in renewable energy certificates (RECs) to meet green energy commitments, without having to undergo renewable energy installations.
Solutions For Effective VRE Integration
In order to overcome the challenges of successfully integrating renewable energy assets into the modern electricity system, grid operators and utilities alike must consider alternative pathways and investments.
Grid Modernization
Grid operators are investing in enhancing transmission infrastructure through digitalization, automation, and AI-driven controls allowing for better renewable integration. Smart grids optimize energy flows, balance loads, and increase flexibility.
Energy Storage Solutions
Battery storage technologies (such as lithium-ion, flow batteries, and pumped hydro) help store excess wind and solar power, making energy from these resources available during periods of low production. These are becoming a critical component of VRE integration.
Demand-Side Management
Utilities and businesses are controlling peak demand by using demand-side management strategies, such as:
- Peak shaving: Reducing energy use during high-demand periods.
- Load shifting: Running operations when electricity costs are lowest.
- Demand response programs: Getting paid to reduce electricity use during grid stress events.
Want To Explore VRE Assets?
As variable renewable energy (VRE) adoption accelerates, integrating wind and solar power effectively into the power grid remains a priority. With ongoing renewable energy trends in 2025 highlighting continued advancements in the industry, now is the time for businesses to explore their renewable energy options. Looking to optimize your energy strategy? Contact our team of energy experts today to explore customized VRE solutions that align with your business goals.